Bronchiectasis Symptoms and Treatment: What You Need to Know to Stay Ahead

What is Bronchiectasis?
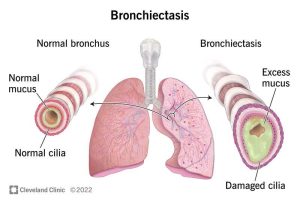
Bronchiectasis is a long-term condition where the airways (bronchi) in the lungs become widened and scarred. These changes make it harder for mucus to clear properly, increasing the risk of infections and further damage. While not as well-known as asthma or COPD, bronchiectasis can be just as disruptive, especially if left untreated.
What Causes Bronchiectasis?
The causes of bronchiectasis can vary widely. In some people, it begins after a severe lung infection such as pneumonia, whooping cough, or tuberculosis. For others, underlying conditions like cystic fibrosis, immune system problems, or allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA) can trigger it. In about 20–30% of cases, the exact cause remains unknown.
Common triggers and causes include:
- Previous lung infections
- Immune deficiencies
- Autoimmune conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or lupus
- Obstruction in the airway from tumours or foreign objects
- Genetic disorders like primary ciliary dyskinesia or cystic fibrosis
If you’ve had repeated chest infections that take longer to clear, especially with a persistent wet cough, it’s worth considering that you may be experiencing bronchiectasis symptoms and treatment should not be delayed.
Related Article: 10 Powerful Bronchiectasis Remedies That Will Transform Your Breathing!
Recognising the Symptoms Early
The earlier bronchiectasis is diagnosed, the better your chances of managing it effectively. Here are some key symptoms:
1. Persistent Cough with Phlegm
A wet or productive cough that lasts for months or even years is the most common symptom. The mucus is often thick and may have a foul smell. Over time, it can change colour and consistency, particularly during flare-ups.
2. Shortness of Breath
As the condition progresses, breathing becomes harder. You may find yourself struggling after light activity or during episodes of infection.
3. Chest Pain and Discomfort
Some people report a feeling of tightness or a dull ache in the chest. This usually results from ongoing inflammation in the lungs.
4. Fatigue
The constant effort of coughing, plus the body fighting off infections, can make you feel exhausted more often than usual.
5. Wheezing and Crackles
Lung sounds like wheezing or crackling may be noticed, especially during breathing exams with a healthcare provider.
6. Frequent Chest Infections
Recurring infections that need antibiotics more than twice a year can be a clear sign of bronchiectasis.
Knowing how these signs link to bronchiectasis causes symptoms and treatment can help you ask better questions during your next GP visit.
Related Article: Managing Bronchiectasis: The Power of Herbal Supplement for Bronchiectasis
Diagnosis: What to Expect
If your doctor suspects bronchiectasis, they will likely start with a chest X-ray, followed by a high-resolution CT scan, which gives a clearer picture of the airways. This scan can confirm the widening of the bronchi and rule out other causes. Other tests may include:
- Sputum cultures to identify bacteria or fungi
- Blood tests for immune function
- Lung function tests to check how well you’re breathing
- Tests for underlying conditions like cystic fibrosis or ABPA
If diagnosed, you’ll be introduced to a treatment plan to manage your bronchiectasis symptoms treatment consistently.
Treatment Options: Managing the Condition Effectively
Bronchiectasis can’t be cured, but symptoms can be controlled and the progression slowed. The treatment approach depends on the underlying cause, severity, and frequency of infections.
1. Airway Clearance Techniques
Clearing mucus is crucial. Physiotherapy methods such as chest percussion, postural drainage, and devices like the Flutter valve or Acapella help loosen and expel phlegm from the lungs.
- Medications
- Antibiotics: Oral or intravenous antibiotics are often used to manage infections. In some cases, long-term low-dose antibiotics may be recommended.
- Bronchodilators: These help open the airways, making it easier to breathe.
- Steroids: Inhaled corticosteroids may be used for those with coexisting inflammation or asthma.
- Mucolytics: These thin the mucus, making it easier to cough up.
3. Vaccinations
Staying up to date with flu and pneumonia vaccines helps reduce the risk of infections that worsen symptoms.
4. Treating the Underlying Condition
For patients with identifiable causes like immune deficiency or ABPA, addressing the root condition is essential to managing bronchiectasis causes symptoms and treatment effectively.
5. Surgery (in rare cases)
Surgical removal of a damaged lung segment may be considered if infections are localised and not responding to other treatments.
Related Article: Foods to Avoid and Foods to Include in a Bronchiectasis Diet
Living Well with Bronchiectasis
Daily management and lifestyle choices make a big difference. While the condition is chronic, people can still live full lives by sticking to a treatment plan and avoiding triggers.
Tips for Daily Management:
- Stay hydrated: Helps keep mucus thin and easier to clear.
- Avoid smoking and second-hand smoke: Smoking worsens lung damage.
- Use a humidifier: Helps keep airways moist, especially in dry environments.
- Monitor your symptoms: Keep a record of cough changes, sputum colour, and infection frequency.
- Exercise regularly: Activities like walking, swimming, or pulmonary rehab improve lung capacity.
If you’re unsure where to begin, reviewing practical steps related to bronchiectasis symptoms treatment can offer a solid starting point for managing daily health.
Related Article: Herbal Remedies for Bronchiectasis: Powerful Plants to Fight Symptoms
What to Watch for in Exacerbations
Exacerbations, or flare-ups, are periods when symptoms suddenly worsen. Early signs may include:
- Increase in the amount or colour of mucus
- Fever or chills
- Worsening shortness of breath
- Chest pain or tightness
- Increased fatigue
Early Herbal Treatment for Bronchiectasis helps prevent permanent damage and keeps you out of hospital. Always contact your GP if you notice a significant change.
Mental and Emotional Wellbeing
Living with a chronic condition can take a toll on mental health. It’s common to feel frustrated or worried about recurring symptoms. Joining a support group, talking to a counsellor, or connecting with others who live with bronchiectasis can help reduce feelings of isolation.
Related Article: How to Manage Bronchiectasis Chest Pain: Natural Treatment Options
When to Seek Medical Help
Contact your healthcare provider if:
- You’re coughing up blood
- You notice severe chest pain
- Antibiotics are no longer working
- You’re experiencing multiple flare-ups in a short time
Taking early action is key in reducing long-term complications and improving your quality of life.
Final Thoughts
Although bronchiectasis is a long-term condition, it doesn’t have to control your life. With early diagnosis, personalised treatment, and regular follow-up, many people live actively and independently. If you’ve recognised any of the symptoms listed here, or already live with the condition, understanding bronchiectasis symptoms and treatment can help you take charge of your health today.
Make sure to speak with your GP about lung health screenings and appropriate vaccinations if you are at risk. And remember, staying informed is your first line of defence.